


Unit 4 in the APUSH Exam
This time period extends from 1800 to 1848 and counts for 10% of recommended instructional content for an AP class.
KEY CONCEPT 4.1
The United States began to develop a modern democracy and celebrated a new national culture, while Americans sought to define the nation’s democratic ideals and change their society and institutions to match them.
KEY CONCEPT 4.2
Innovations in technology, agriculture, and commerce powerfully accelerated the American economy, precipitating profound changes to U.S. society and to national and regional identities.
KEY CONCEPT 4.3
The U.S. interest in increasing foreign trade and expanding its national borders shaped the nation’s foreign policy and spurred government and private initiatives.
OVERVIEW
AP U.S. History Period 4 focuses on the time period from the election of 1800 to the end of the Mexican-American War in 1848. Period 4 is primarily a period of gradual change that lays the foundation for later periods.
By this point in American history, the U.S. Constitution was firmly the law of the land. However, the new country needed to figure out the limits of the Constitution and work to shape itself into a modern democracy. One of the first steps was to establish the idea of judicial review as a way for the judicial branch to check the power of the legislative and executive branches. American democracy also expanded its democratic participation to gradually include all [free] men.
Beginning in the early 1900s, Americans also began to think of themselves as Americans—not British, or colonists, or settlers in different communities. As part of this movement, artists began to use distinctly American styles to paint landscapes. Likewise, a distinctive American religious identity started to emerge in the Second Great Awakening.
Economically, the United States began to change from an agricultural economy to a manufacturing economy. There were several important inventions during this time that helped the transition, including the invention of the telegraph and textile machinery. Henry Clay’s American System ensured that goods and services could move quickly around the country. The North gradually became a major industrial center. The South maintained its agricultural character with large plantations fueled by slave labor. While the division between the North and South started with these economic differences, the two areas gradually came to develop distinct cultural identities and worldviews.
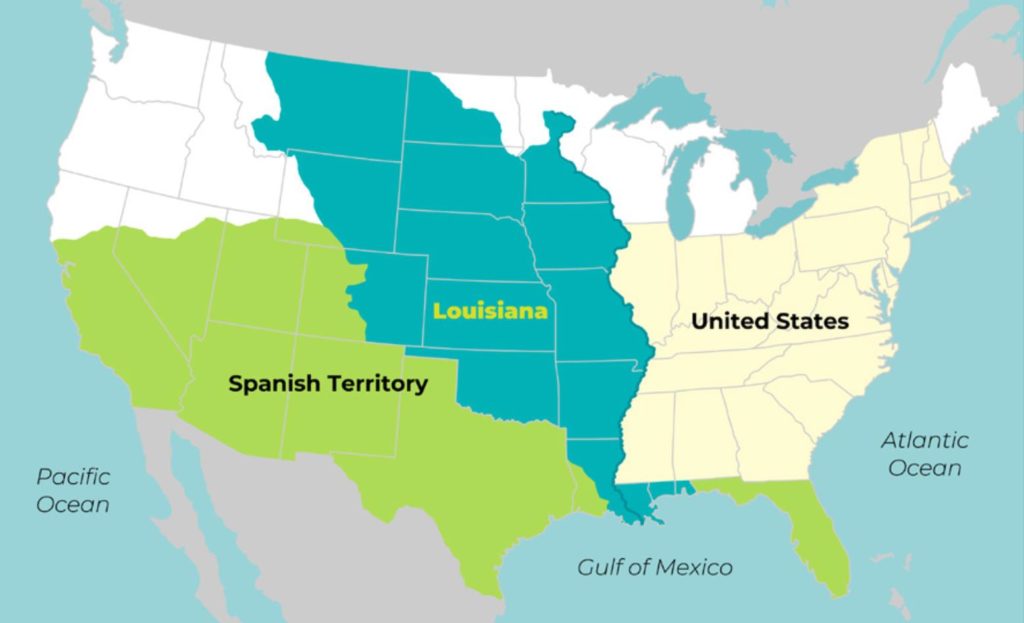
Americans continued to expand westward. As a result of this, Native Americans were continually displaced and treated unfairly by the federal government. Many were forcibly relocated onto reservation lands in Oklahoma and the American southwest. The federal government purchased the Louisiana Territory from France in 1803 and doubled the size of the country overnight.
TIMELINE
1803 The federal government finalizes the Louisiana Purchase.
1807 Congress votes to end the international slave trade.
1812 The U.S. declares war against Britain.
1820 The Missouri Compromise was the first federal compromise to try to balance slave and free states.
1823 President James Monroe declared the Western Hemisphere closed to European colonization in The Monroe Doctrine.
1830 Andrew Jackson signed the Indian Removal Act to relocate American Indians west of the Mississippi River.
1845 The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass was published.
1848 The first women’s rights convention was held in Seneca Falls, New York.
KEY TERMS
Judicial Review The ability of the Supreme Court to determine whether a law is constitutional.
Second Great Awakening A series of religious revivals in the early 1800s that focused on personal religious experience.
American System A plan proposed by Henry Clay that was intended to strengthen the economy of the U.S. through a combination of tariffs, national banks, and infrastructure.
Louisiana Territory A large portion of land that was purchased from France by the U.S. Federal government in 1803 for $15 million.
The best way to get better at something is by practicing.
That’s why it’s so important that you take practice tests to help you get better at the AP European History Exam. Only then can you expect to get a good score—and even improve your score.
Download your free AP® European History practice test HERE.
Download your printable study guides for all of the units for AP European History HERE.
 Help
Help